Early Impacts of Pandemic Suggest an Abrupt About-Face for the Remodeling Market

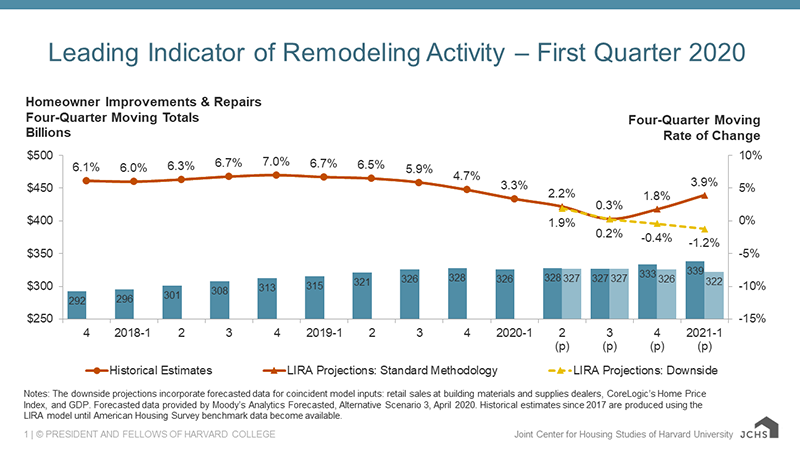
CAMBRIDGE, MA – Owner expenditures for home renovations and repairs are expected to decline at least through the first quarter of next year due to fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic, according to the Leading Indicator of Remodeling Activity (LIRA) released today by the Remodeling Futures Program at the Joint Center for Housing Studies of Harvard University. Pre-pandemic, the LIRA pointed to a healthy rebound in home remodeling spending with annual growth of 3.9 percent by the first quarter of 2021, but the latest data incorporating both actual and forecasted impacts of the economic shutdown point to spending declines this year with further worsening into 2021.
“While there is still considerable uncertainty surrounding the near- and longer-term impacts of the pandemic, the best available evidence suggests substantial downturns in key remodeling indicators of new home construction, home sales and values of existing homes over the coming quarters,” says Chris Herbert, Managing Director of the Joint Center for Housing Studies. “Homeowners who are concerned about losses of income, home equity, and other forms of wealth are anxious about making large investments in improving their homes in this economic environment.”
With the unprecedented changes to the US economy since mid-March, the Remodeling Futures Program is providing a downside range for the home remodeling outlook, which incorporates forecasts for several core model inputs—retail sales of building materials, home prices, and GDP. “Quarterly spending for improvements and repairs to the owner-occupied housing stock is projected to turn negative by the third quarter, and annual expenditures are expected to fall to $322 billion by early next year with potential for even more severe declines to follow,” says Abbe Will, Associate Project Director in the Remodeling Futures Program at the Center. “Beyond the start of next year, remodeling activity that would typically result from expanding homebuilding, sales of existing homes, and home prices mean the greatest downturn could come later in 2021 with recovery depending on what occurs in housing markets over the remainder of this year.”
Click image for full-size chart.
The Leading Indicator of Remodeling Activity (LIRA) provides a short-term outlook of national home improvement and repair spending to owner-occupied homes. The indicator, measured as an annual rate-of-change of its components, is designed to project the annual rate of change in spending for the current quarter and subsequent four quarters, and is intended to help identify future turning points in the business cycle of the home improvement and repair industry. Originally developed in 2007, the LIRA was re-benchmarked in April 2016 to a broader market measure based on the biennial American Housing Survey.
The LIRA is released by the Remodeling Futures Program at the Joint Center for Housing Studies of Harvard University in the third week after each quarter’s closing. The next LIRA release date is July 16, 2020.
The Remodeling Futures Program, initiated by the Joint Center for Housing Studies in 1995, is a comprehensive study of the factors influencing the growth and changing characteristics of housing renovation and repair activity in the United States. The Program seeks to produce a better understanding of the home improvement industry and its relationship to the broader residential construction industry.
The Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies advances understanding of housing issues and informs policy. Through its research, education, and public outreach programs, the Center helps leaders in government, business, and the civic sectors make decisions that effectively address the needs of cities and communities. Through graduate and executive courses, as well as fellowships and internship opportunities, the Center also trains and inspires the next generation of housing leaders.
Contact: Kerry Donahue, (617) 495-7640, [email protected]